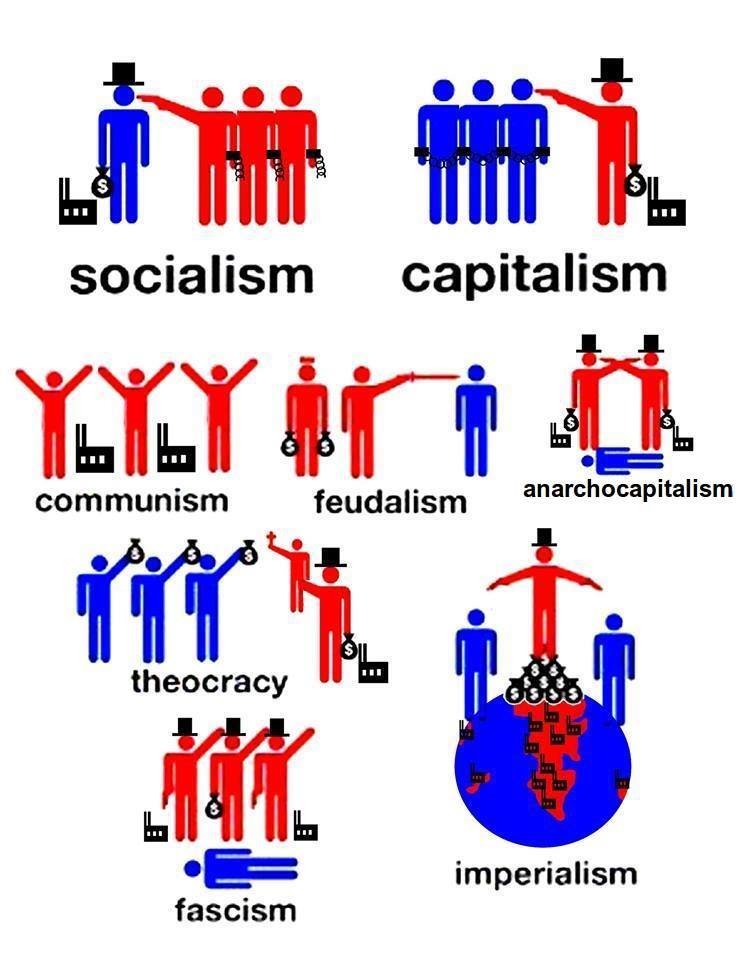
The most Influential economical and political theories of the world short notes on capitalism , socialism, fascism , communism
Capitalistic
- Capitalistic ownership means private entities own factors of production. and derive their income from their ownership.
- goods and services are distributed according to the laws of supply and demand.
- The government role is to protect the free market.
- Capitalism makes an economy produce the most desired products at an acceptable price.
- Capitalism doesn't provide for those who lack competitive skills. This includes the elderly, children, the developmentally challenged and their caretakers
- Capitalism does not promote equality of opportunity.
eg. USA ,Canada ,Chile, Germany
SOCIALISM
- Founder of Modern Socialism By Karl Marx in 1848
- Goal of socialism is to eradicate class system and reach the Utopian socialist model by Henri de Saint-Simon
- Socialism is an economic system where everyone in the society equally owns the factors of production.
- economic activities are carried on mainly for social gains and personal interest is of less significance.
- democratically-elected government has the ownership.
- It could also be a cooperative or a public corporation where everyone owns shares.
- Everyone in society receives a share of the production based on how much each has contributed.
- Workers are no longer exploited, since they own the means of production
- Socialism relies on cooperative nature of humans to work.
- corruption, and lack of incentive for workers to produce, have reduced production and the average standard of living.
- According to Marx socialism is in between between capitalism and communism.
- Two types of Socialism -
- 1. Marxism–Leninism
- 2. Social Democracy
- Social democracy is a kind of socialism that tries to mix parts of socialism with capitalism. In this system, the government takes wealth (money) from the rich and gives it to the poor like in a Communist state, but despite there being more government control and less chance to make a very large amount of money, people can still run their own businesses and own private property.
- example, education, health care, housing, utility companies and public transportation
- Collectivization
In this system, money and goods are shared more equally among the people, with the government in control. In theory, this system results in the gap between classes getting smaller, with the poorest of a nation's people being helped by the state while the richest agree to higher taxes and economic controls/restrictions.
eg. India ,Norway, Sweden, and Denmark partial socialist country
Fascism
- Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini founder of Fascism.
- Fascism uses this nationalism to override individual self-interest.
- It legitimizes any studies that support the concept of national characteristics and the superiority of the nation's majority race
- The leader assumes the role of the father of the nation. He creates a cult status as a "dauntless ruler beholden to no one."
- The state violently persecutes minority groups and opponents.
- Fascism only aids those who align with the national values. They may use their power to rig the system and create additional barriers to entry.
- Fascism ignores external costs, such as pollution. This makes goods cheaper and more accessible. It also depletes natural resources and lowers the quality of life in the affected areas
- eg.
- Italy (1922–1943)
- Germany (1933–1945)
- Japan (1931–1945)
Communism
- the Communist Manifesto, written by Karl Marx with Friedrich Engels and published in 1848.
- Class struggle to be removed, which promotes
- Abolition of property in land and application of all rents of land to public purposes.
- A heavy progressive or graduated income tax.
- Abolition of all right of inheritance.
- Equal liability of all to labor. Establishment of industrial armies especially for agriculture.
- Free education for all children in public schools. Abolition of children's factory labor. The combination of education with industrial production.
- difficult for the planning group to get up-to-date information about consumers' needs.
- eg. China, Vietnam, Laos, Cuba, and North Korea.


Comments
Post a Comment