Which Missiles Does the Indian Army Use? || Everything You Need to Know about India's Missile Program
Missiles are one of the most important pieces of equipment owned by any country's armed forces. India is no exception. But the thing is that there is a lot of confusion about the different types of missiles, how they work, their speed, their target hitting abilities, their effective range etc. This article will help you understand everything that you need to know about missiles and India's Missile Program.
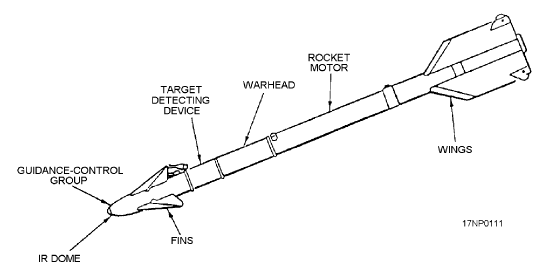
Missiles have a number of different system components:
Shorter range ballistic missiles stay within earth atmosphere whereas long-range ones travel most of their flight out of atmosphere.
The flight operation consists of the following parts:
Cruise Missiles are propelled by jet engines or turbo fan for high speeds and low altitude trajectory.
What are missiles?
Missiles are self propelled, guided weapons which travel through air to strike the enemy target. Trough-Weight is the total weight of the missile except the launch rocket and fuel. It is measured in KG or Tonnes.Missiles have a number of different system components:
- Guidance system
- Targeting system
- Flight system
- Engine
- Warhead
Parts of a missile
Missiles can be categorised by size, speed and range, and whether launched from land, air, surface ship, or submarine. Often versions of the same missile are produced for different launch platforms; sometimes air- and submarine-launched versions are a little lighter and smaller than land- and ship-launched versions.Ballistic missiles
A ballistic missile follows a ballistic trajectory that is similar to projectile motion.Shorter range ballistic missiles stay within earth atmosphere whereas long-range ones travel most of their flight out of atmosphere.
The flight operation consists of the following parts:
- Powered flight portion: Where the weapon gathers the momentum and direction.
- Free flight: It takes assistance of gravity and air resistance.
- Re- entry: This phase is exclusive for long range missile like ICBM's, here missile renters the atmosphere.
Types of ballistic missiles
Cruise Missiles
These missiles take off like a aircraft, travelling at constant speed, extremely low altitude trajectory. Cruise missiles are well known for their marked precision.Cruise Missiles are propelled by jet engines or turbo fan for high speeds and low altitude trajectory.
Types
1. On basis of speed
( Mach number= Speed of object/Speed of sound Speed of sound= 343 m/s)
The Agni Missile was initially conceived in the IGMDP as a technology demonstrator project in the form of a re-entry vehicle but was later upgraded to a ballistic missile with different ranges.
After completion of IGMDP, India has decided to develop future missiles as independent projects with possible collaboration with private or foreign partners.
With dedicated teams of scientists, engineers and hard work, India has been able to develop a good range of missiles.
Must Read : Everything you need to know about Nuclear Non Proliferation Treaty
2. On basis of distance
- Short range: Upto 300 km.
- Medium range: Upto 1000 km.
- Long range: Beyond 1000 km.
Ballistic missile V/s Cruise missile
- A cruise missile locates its target or has a preset target, and navigates there whereas a ballistic missile is targeted as a projectile from a single launch force with not much-added guidance.
- Ballistic missiles travel at very high altitude whereas cruise missiles follow a flat trajectory close to ground.
- With high speed ballistic missiles are harder to intercept than cruise missiles.
- Cruise Missiles have greater accuracy and precision.
India's missile program
Post independence missile history of India begins in 1958, when the government of India constituted a team of Indian scientists called the Special Weapons Development Team with an aim to research on guided missile weapons development.Integrated guided missile development programme (IGMDP)
The IGMDP was launched in 1982 under the leadership of former president Dr. A.P.J Abdul Kalam who achieved the fame of being known as missile man of India. IGMDP was managed by DRDO and ordnance factory boards. The project aimed to develop:- Short range surface-to-surface missile.
- Short range low-level surface-to-air missile.
- Medium range surface-to-air missile.
- Third-generation anti-tank missile.
Nag anti tank missile
The Agni Missile was initially conceived in the IGMDP as a technology demonstrator project in the form of a re-entry vehicle but was later upgraded to a ballistic missile with different ranges.
After completion of IGMDP, India has decided to develop future missiles as independent projects with possible collaboration with private or foreign partners.
With dedicated teams of scientists, engineers and hard work, India has been able to develop a good range of missiles.
India's Missile Arsenal
Projects under development
India is developing Brahmos II, which will be a hypersonic version of the original Brahmos missile with a range of 450 km. Agni VI is also being developed which will have a range of 8000km to 12000km. |
| Image Source - missiledefenseadvocacy.org |
India's nuclear triad
India is one of the few countries which are capable of launching nuclear missiles from land, water and air which was achieved with the commissioning of INS Arihant which carries K-15 missiles.Must Read : Everything you need to know about Nuclear Non Proliferation Treaty


Comments
Post a Comment